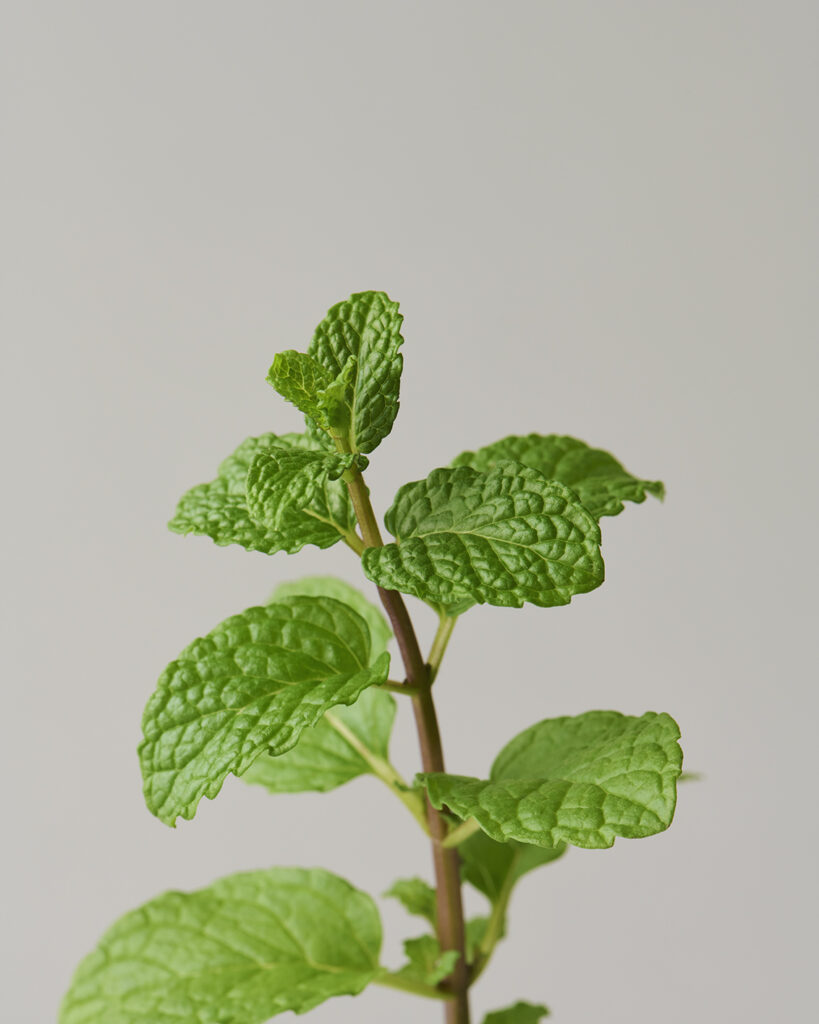
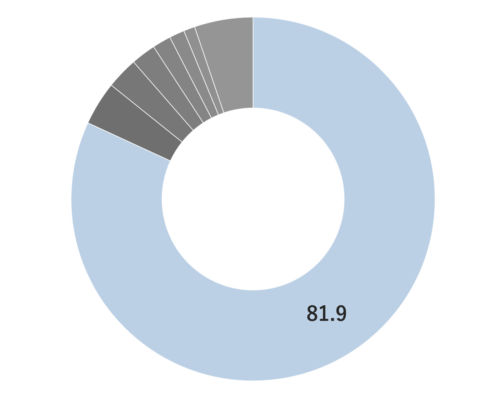
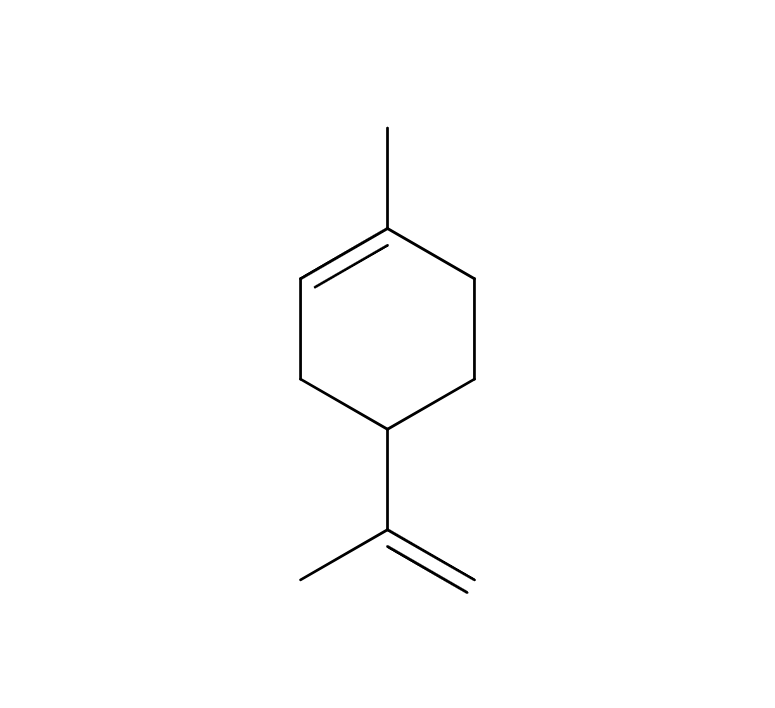
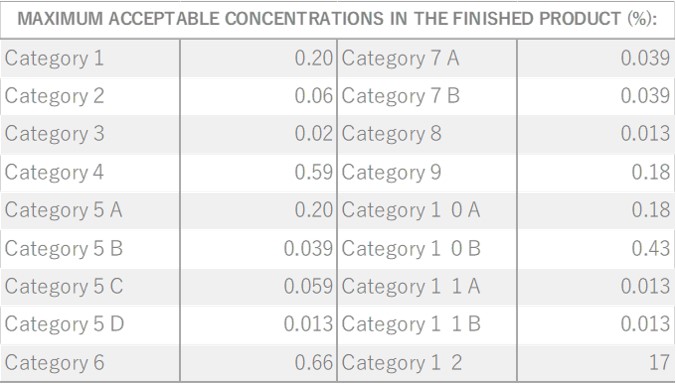
Spearmint is a perennial herb of the Lamiaceae family that grows to a height of 30-60 cm. . It produces white to light purple flowers at the ends of its stems, a display that occurs from summer through fall. The herb is known for its short, opposite, serrated leaves with a slightly rounded shape, resembling the tips of spears. This unique leaf shape contributes to its name “spear.” Additionally, its scientific name, “spicata,” is derived from the ear-shaped flower spikelets found at the tip of its stems. Spearmint is believed to be a hybrid of Peppermint and Water Mint and is sometimes referred to as Dutch Mint or Curly Mint. Among more than 1,000 varieties of mint, it is characterized by a less intense aroma. Spearmint is widely utilized in daily life as a flavor enhancer in cooking, teas, and various everyday products.