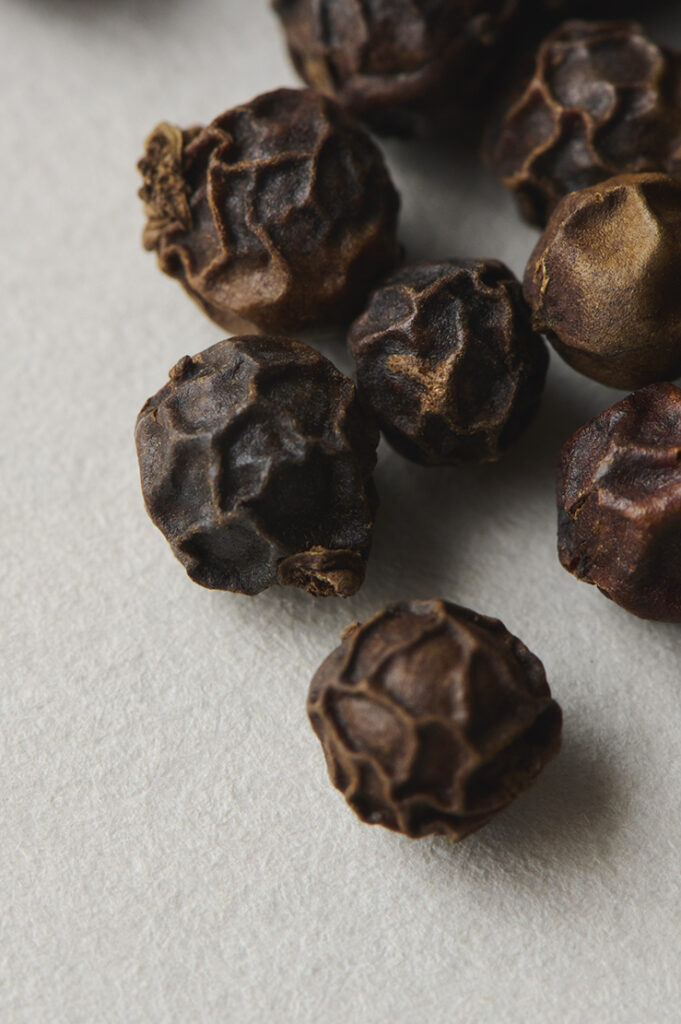
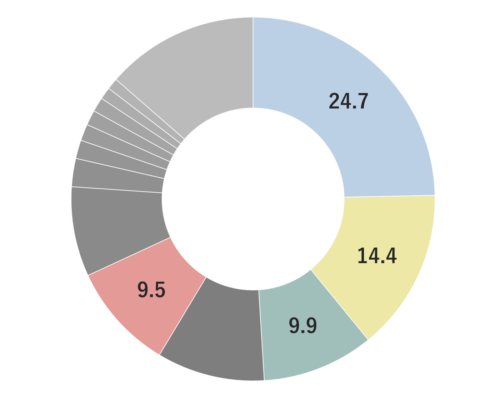
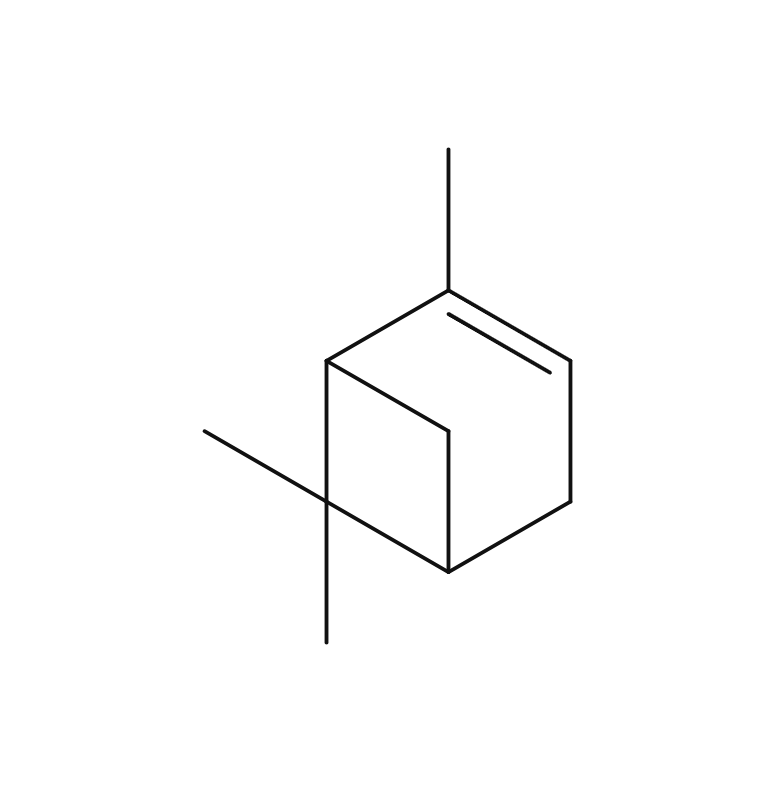
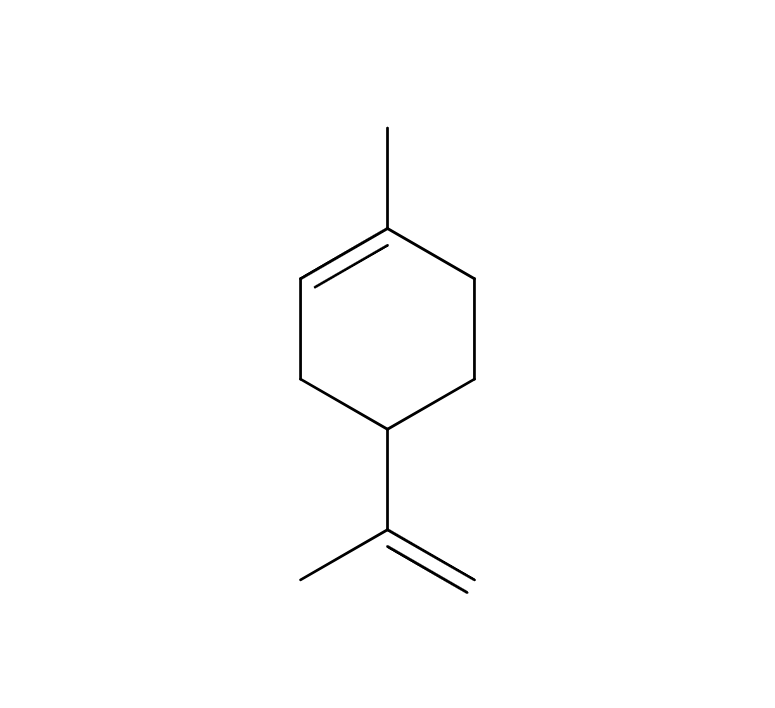
Black Pepper is a perennial vine of the pepper family, growing up to 10 meters long. It produces small, spherical fruits, known as peppercorns, typically ranging from 3-6 mm in size. Initially green, these peppercorns turn red and eventually mature into a black color. Depending on the processing method, various types of pepper can be obtained, with the most familiar one being Black Pepper, which is achieved by drying the berries before full ripening. It has a rich history that spans over 4,000 years, with applications in traditional medicine, particularly in Ayurveda. There is a theory suggesting that during medieval times, black pepper was as valuable as gold in Europe, contributing to the Age of Exploration due to its soaring demand.