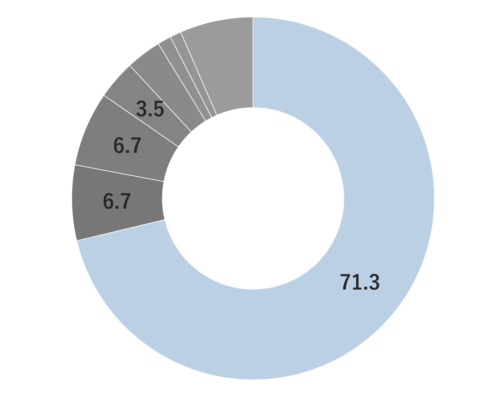
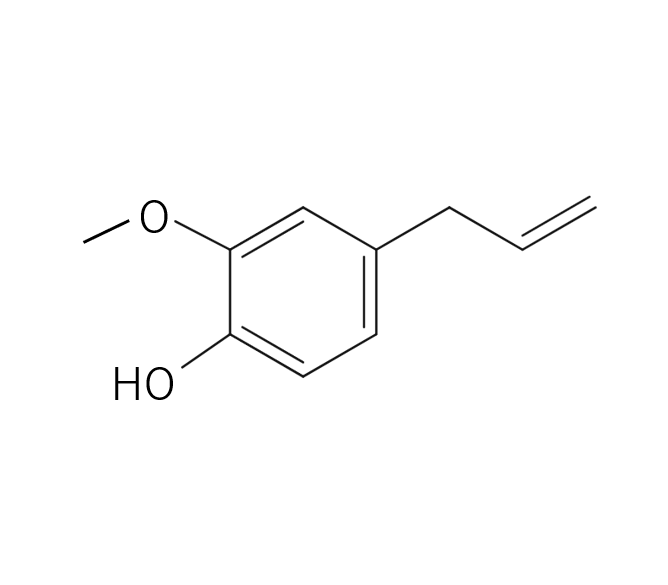
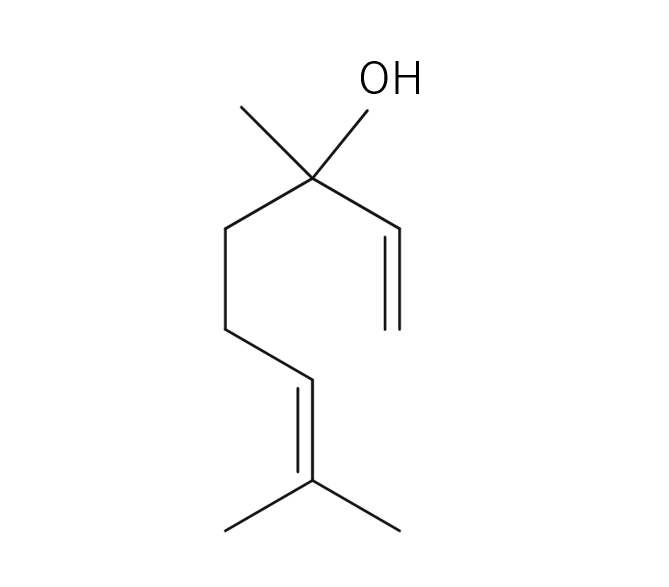
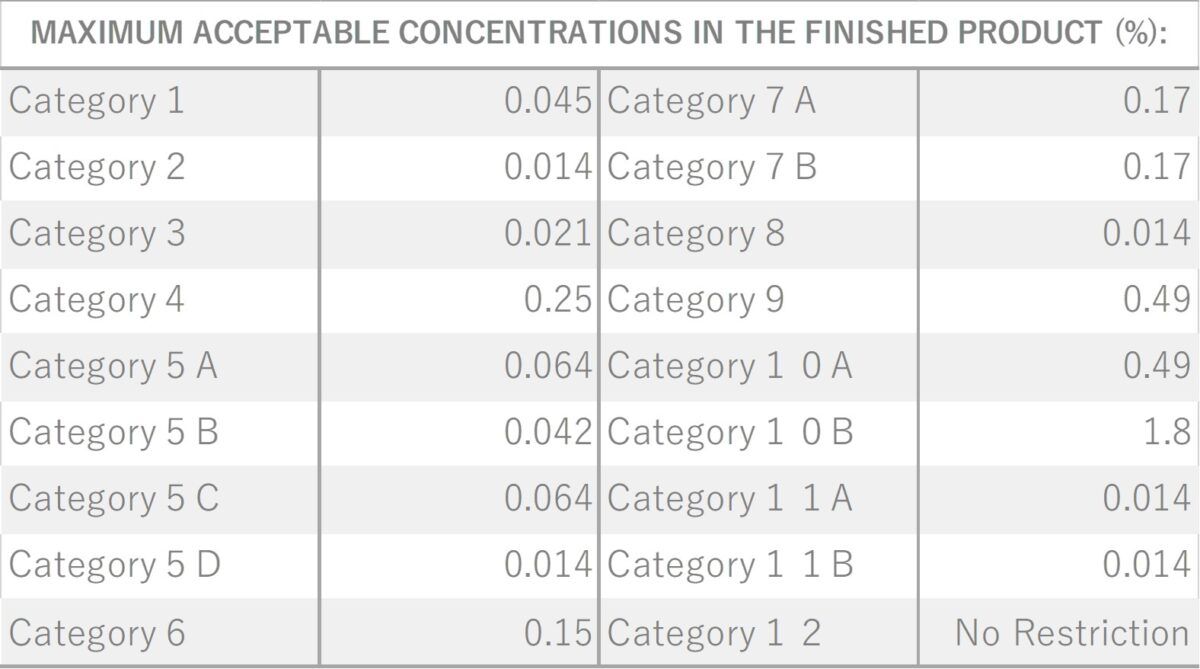
- References
- Jennie Harding [Handbook of Essential Oil and Plant Oil] Tokyo-do Publishing, 2010.
- Shinichiro Otsuki/Yukiko Ozaki [Scientific Name Etymology Dictionary of Herbs] Tokyo-do Publishing, 2009.
- Jennie Harding [Illustrated Reference Book of Herbs] Sancho Publishing, 2012.
- Freddy Ghozland/Xavier Fernandez [L’Herbier Parfume] Hara Publishing, 2013.
- Kyohei Mikami [Comprehensive Guide to Essential Oils] Fragrance Journal, 2010.
- Yuzuru Ogura [Dictionary of Plants] Tokyo-do Publishing, 1957.
- Nobuo Ohashi [Dictionary of Medical Herbs] Tokyo-do Publishing, 2016.
- Wanda Sellar [The directory of essential oils] Fragrance Journal, 1992.
- Aroma Environment Association of Japan [AEAJ Aromatherapy Certification Official Textbook grade1&2] Sekaibunka, 1999.
- Robert Tissearand [Essential Oil Safety] Fragrance Journal, 2018.
- Ayako Berg [Aromatherapy Essential Oil Dictionary] Seibido Shuppan, 2022.
- Azusa Annells [Enjoying Fragrance: An Illustrated Book of Aromas with Characteristics]Natsumesha CO.,LTD., 2023
- International Fragrance Association, Cinnamic aldehyde,2020.
- International Fragrance Association, Linalool, 2004.
- Supervisor
- Yamamoto Perfumery co., ltd.