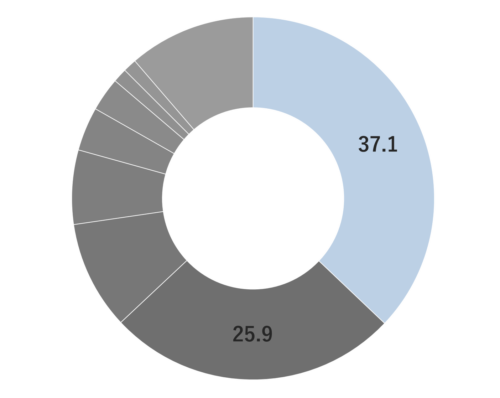
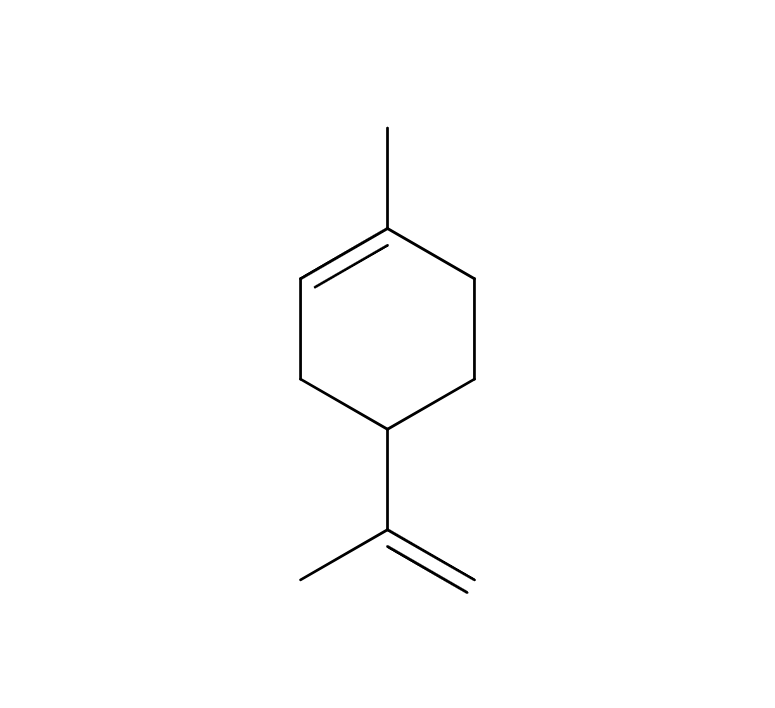
Peppermint, a perennial herb belonging to the Lamiaceae family, reaches a height of about 10 cm. It boasts light purplish-pink flowers, robust dark green stems, and serrated green leaves. The mint genus displays significant variability, featuring numerous varieties with diverse leaf colors and fragrances. Among the key species are: 1) Black mint (M. piperita var. vulgaris Sole), 2) White Mitcham (M. piperita var. officinalis Sole), and 3) M. piperita L., the botanical foundation of the genus, believed to be a natural hybrid of watermint and spearmint. Its scientific name, “piperita,” signifies “peppery,” reflecting its remarkable pungency in comparison to other mint varieties. Peppermint is extensively cultivated in Europe.