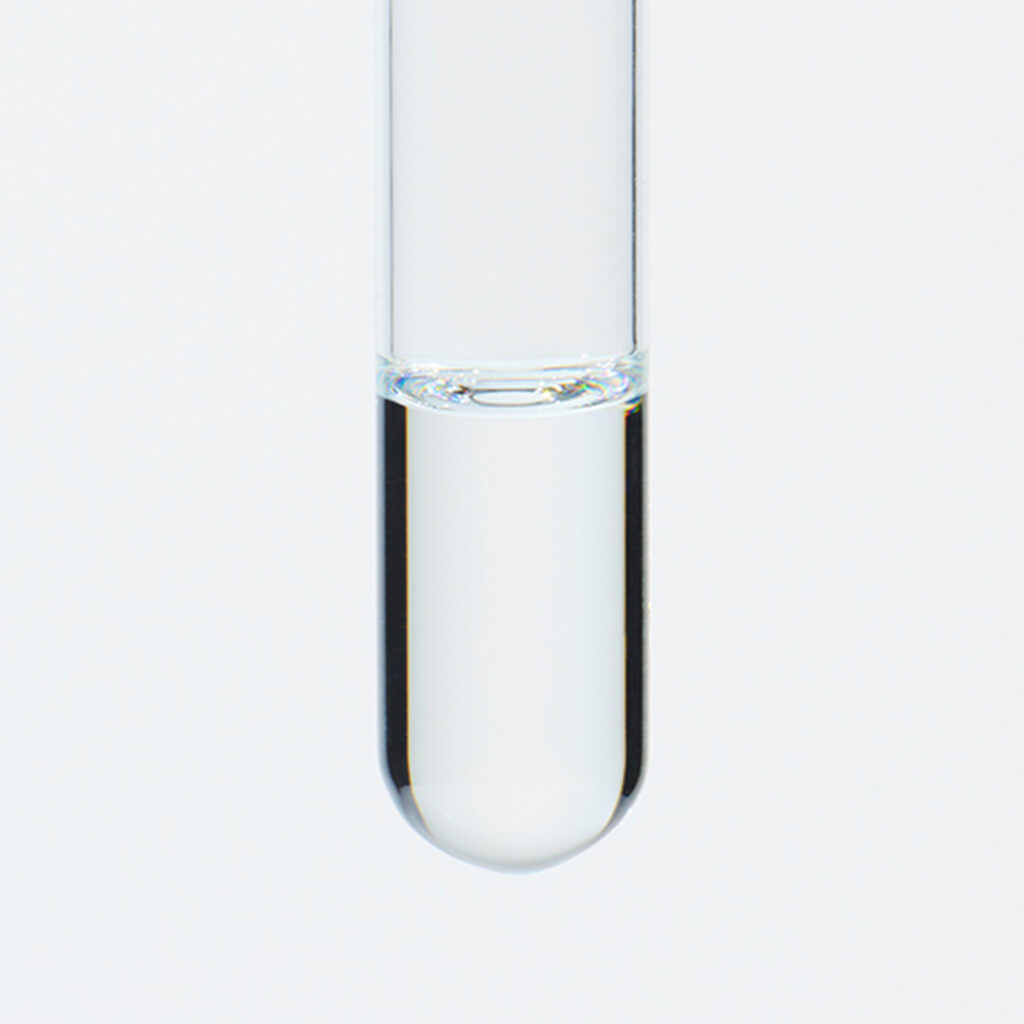
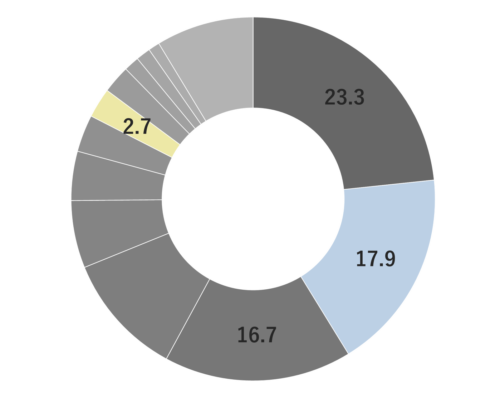
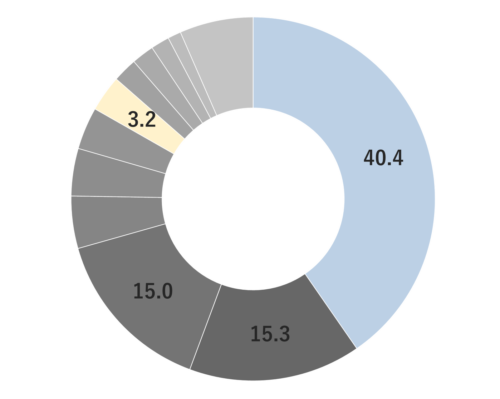
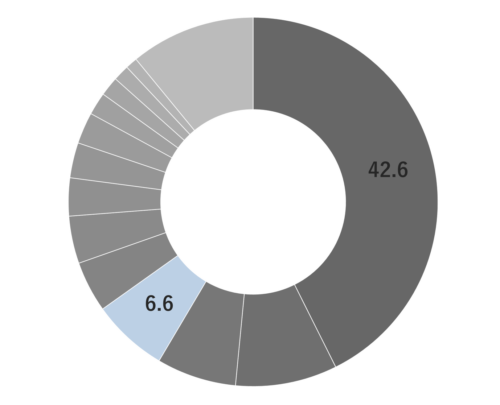
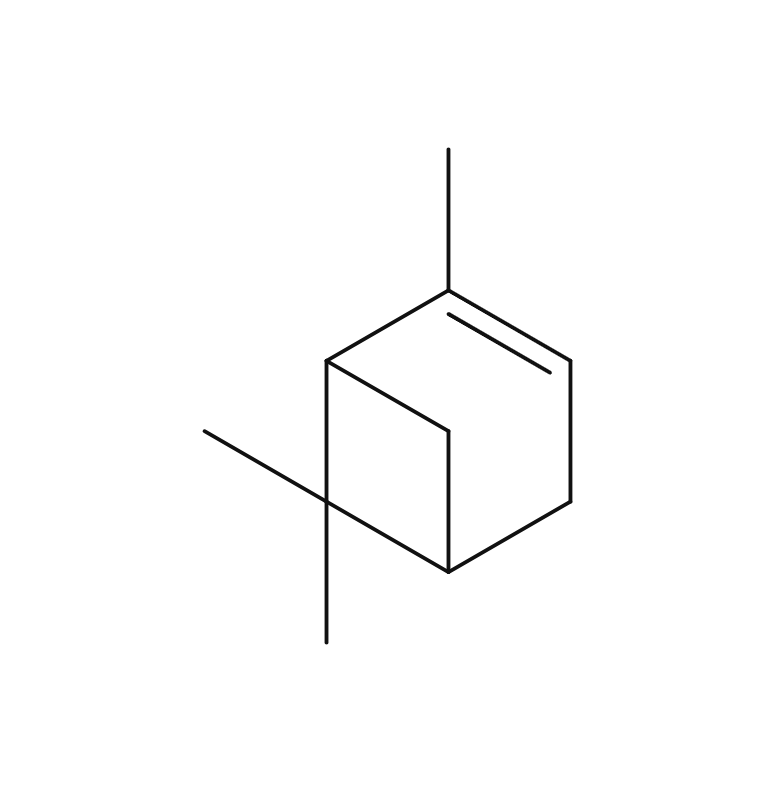
About 0.3-0.5% of Rosemary essential oil is obtained by steam distillation from its stems and leaves, and is colorless and clear in color. It is characterized by the presence of borneol, which imparts a subtly sweet, camphor-like aroma. Rosemary essential oil can be found in three main chemotypes: camphor-rich, cineole-rich, and verbenone-rich, each offering a unique fragrance profile. The cineole-rich variety, known as Rosemary Cineole, provides an invigorating and crisply clean sensation, with subtle sweetness and a calming overall impression.Rosemary Cineole blends harmoniously with essential oils that possess a sweet and deep character, such as Cedarwood, Petitgrain, and Frankincense. When it comes to creating aromatic accords, it pairs well with basil, lavender, minty scents, lemongrass, and petitgrain, making it a versatile option for fragrance blending.