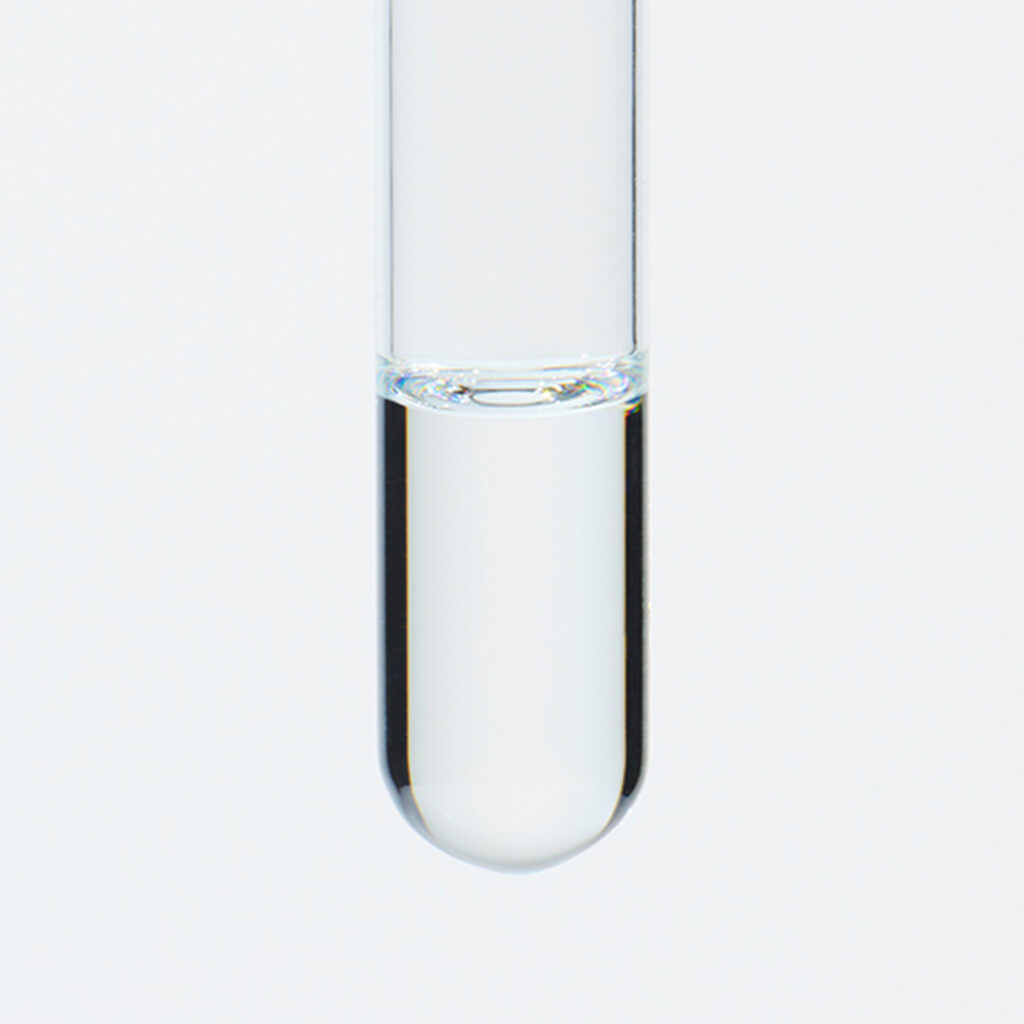
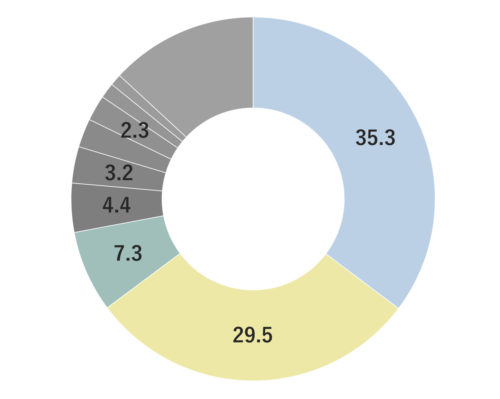
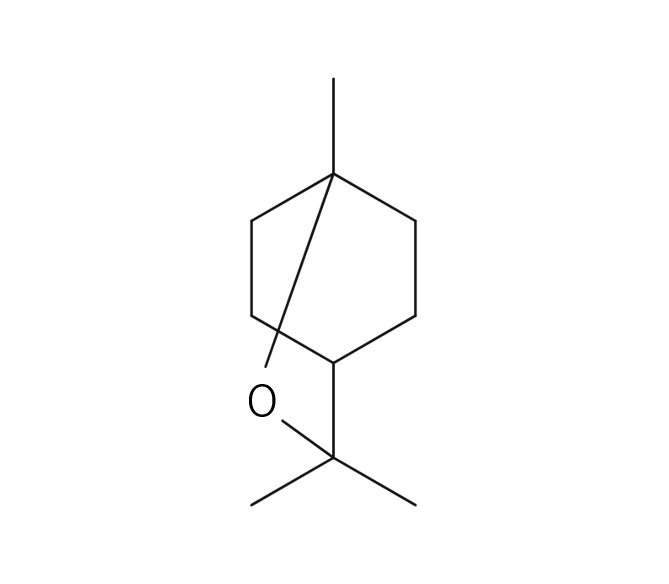
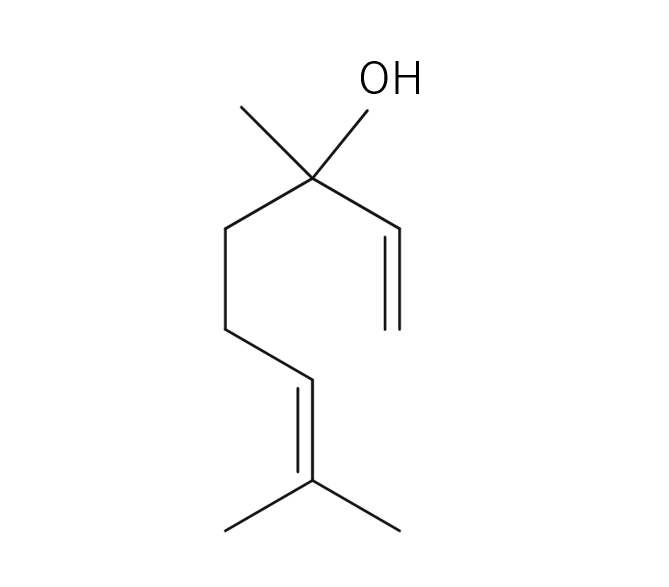
About 1.5%-2% of Lavandin essential oil is obtained by steam distillation from Lavandin flowers and is colorless to pale yellow in color. Its primary constituents include linalool, known for its relaxing properties, along with linalyl acetate and camphor, among others. Lavandin essential oil is distinguished by its fresher and sweeter aroma compared to lavender essential oil. The fragrance carries the sweetness characteristic of lavender, but also possesses an herbal freshness that sets it apart. This combination of scents makes Lavandin a versatile choice, appealing to those who may not favor lavender. Lavandin essential oil is a key ingredient in various products, particularly in eau de cologne and men's cosmetics. It blends harmoniously with a wide range of other essential oils and pairs exceptionally well with numerous citrus oils. Due to its neutral strength, it's recommended add in amounts that maintain a well-balanced blend.