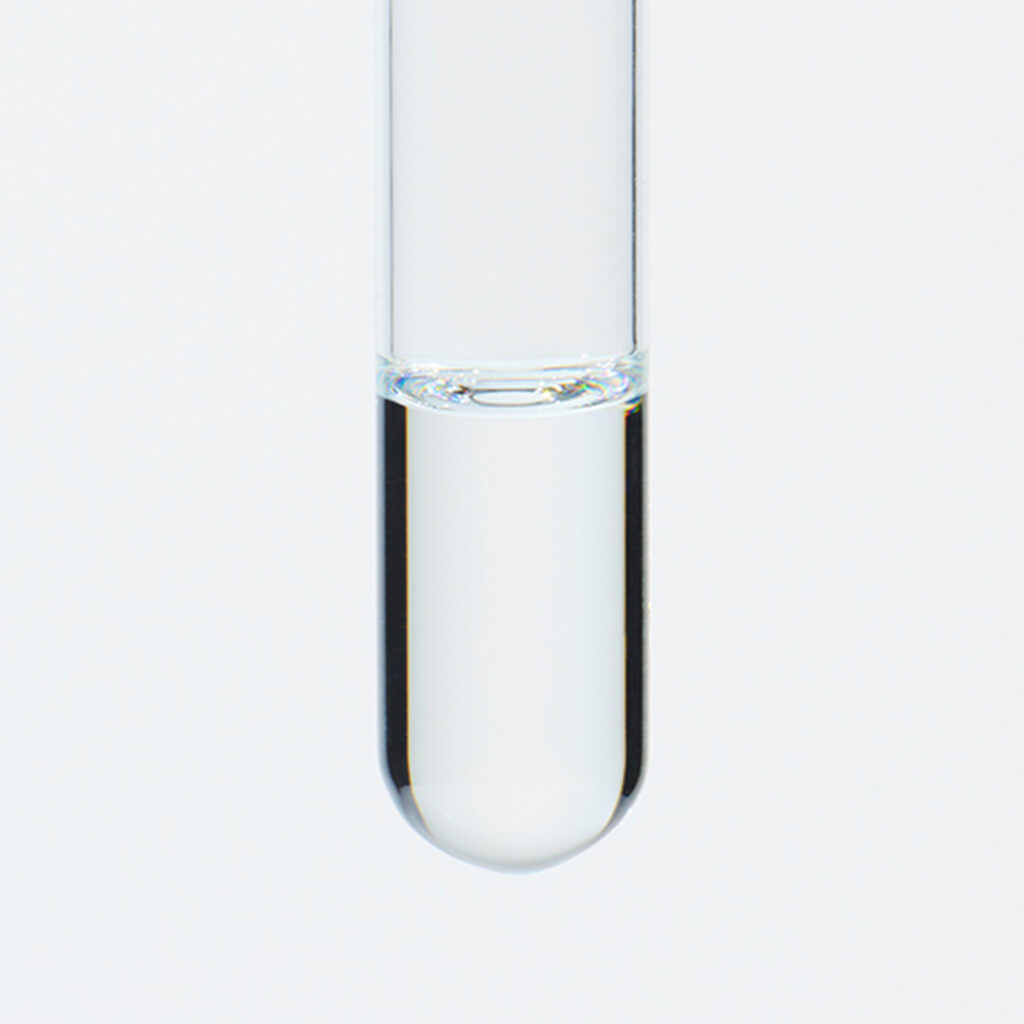
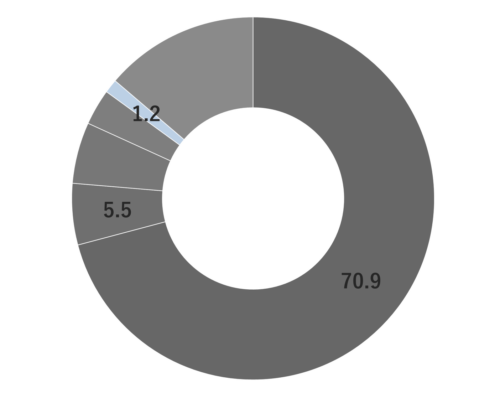
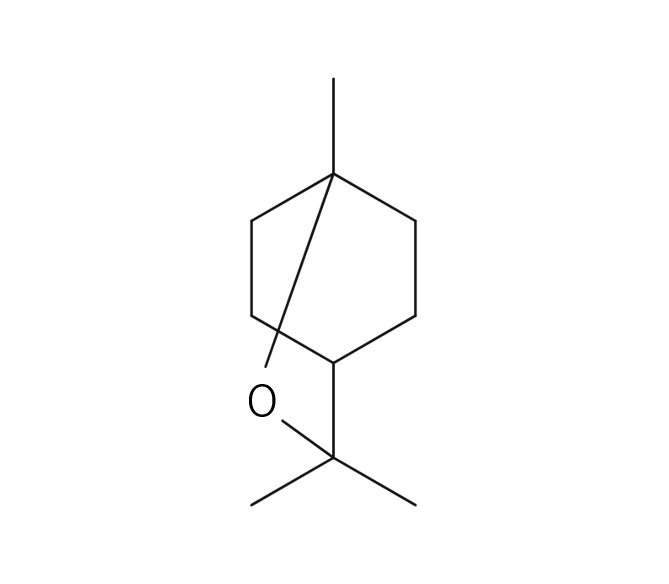
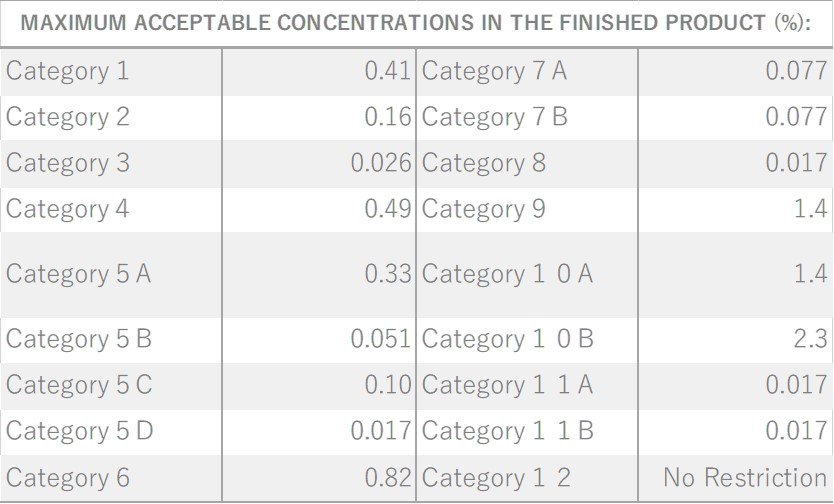
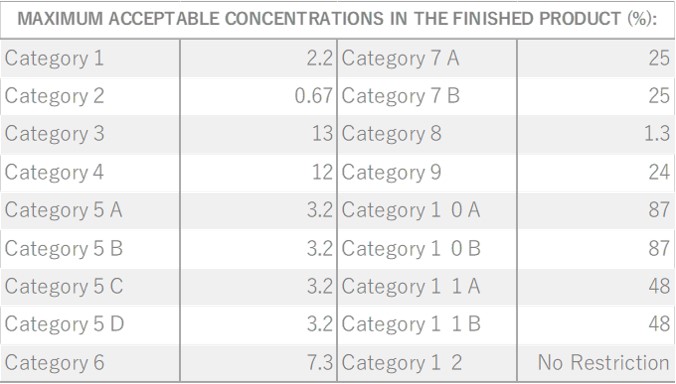
About 0.5-0.7% of Eucalyptus Citriodora essential oil is obtained from its leaves by steam distillation, light yellow to yellow in color. While the oil yield may be slightly lower compared to essential oils from other eucalyptus species, its distinctive composition sets it apart. The primary component is 1,8-cineole, also known as "eucalyptol," which imparts a refreshing, cool, and throat lozenge-like aroma.It is particularly rich in citronellol, known for its insect-repelling properties, contributing to the oil's lemon-like fragrance. It is popular for its refreshing, slightly sweet, and clear characteristics. The oil harmonizes seamlessly with citrus and woody essential oils, making it an excellent companion for lemony scents. Additionally, it pairs well with Ylang-Ylang, known for its strong sweetness. Despite its neutral strength, it's recommended add in amounts that maintain a well-balanced blend.