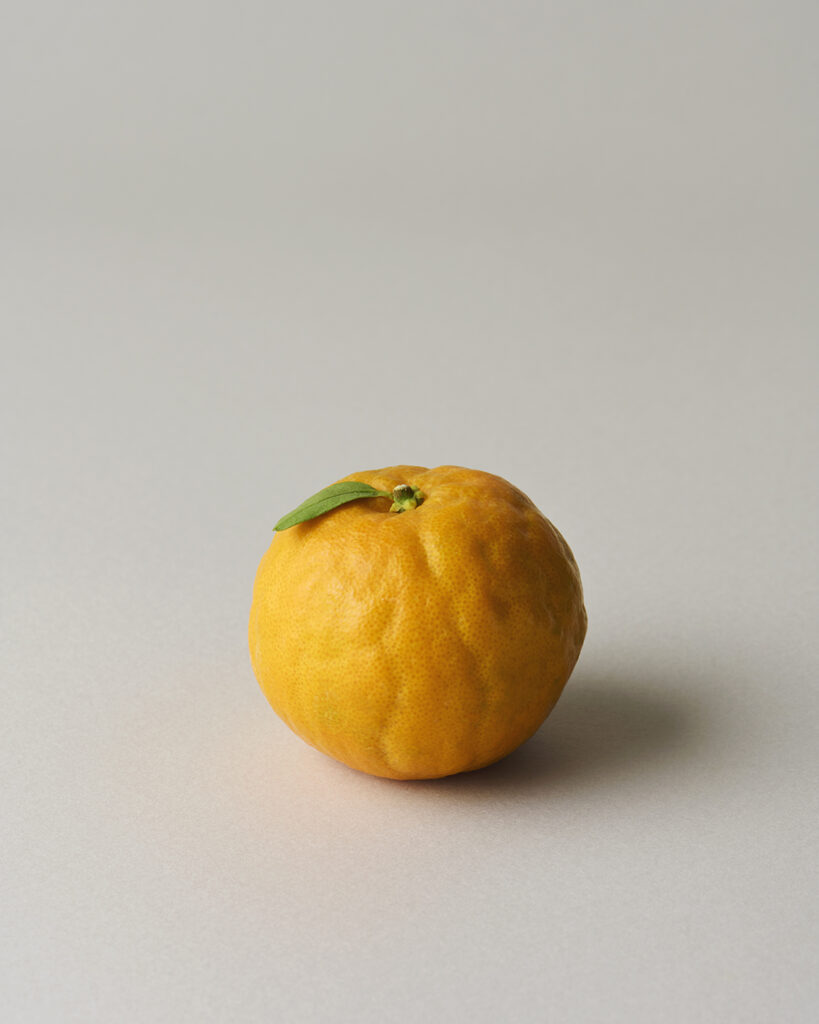
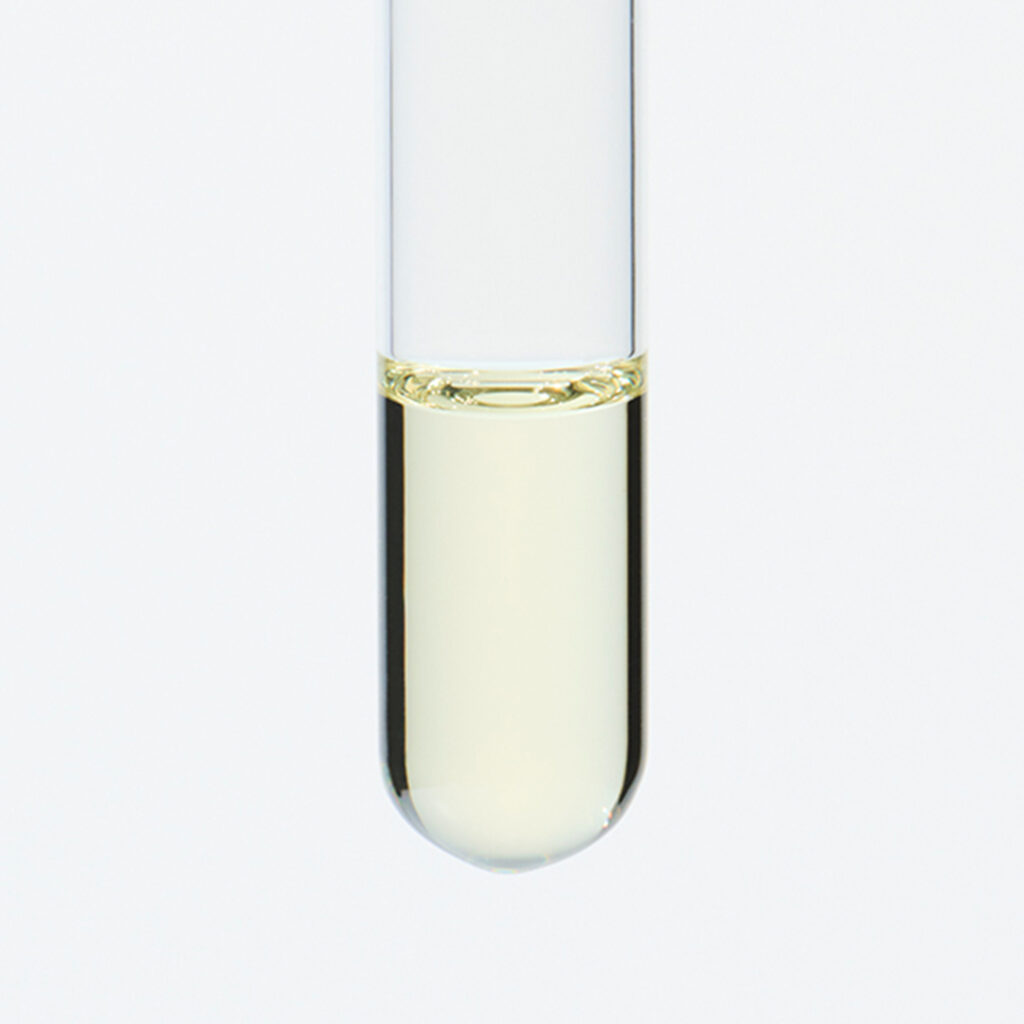
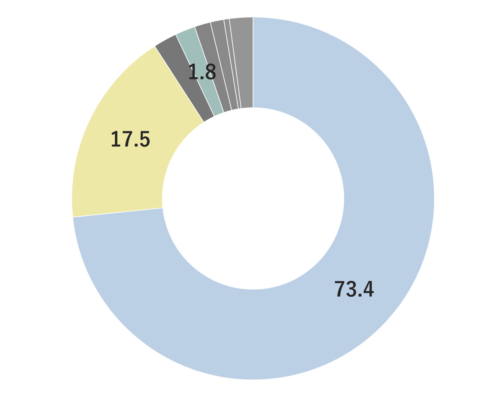
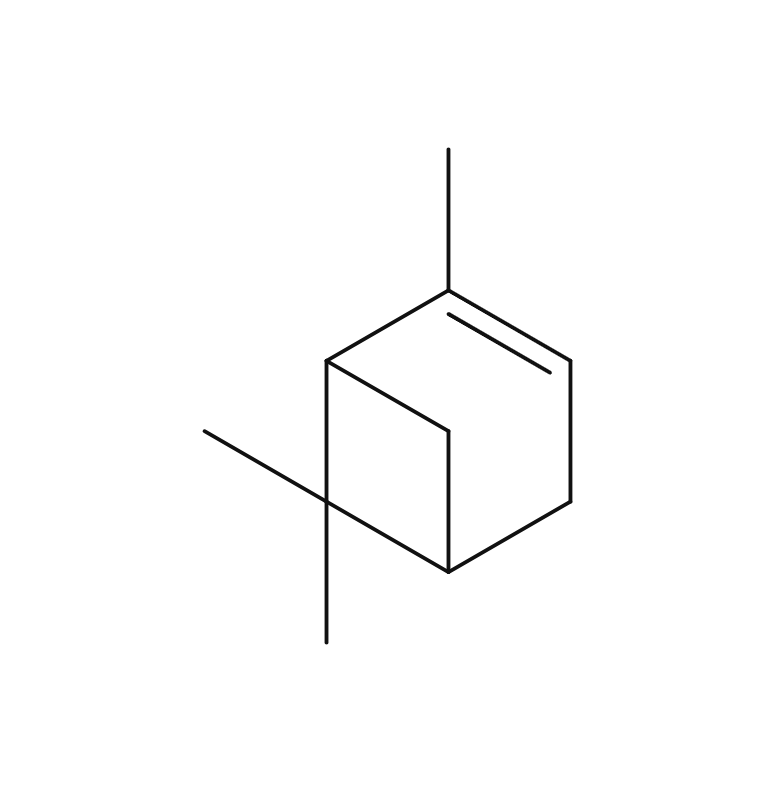
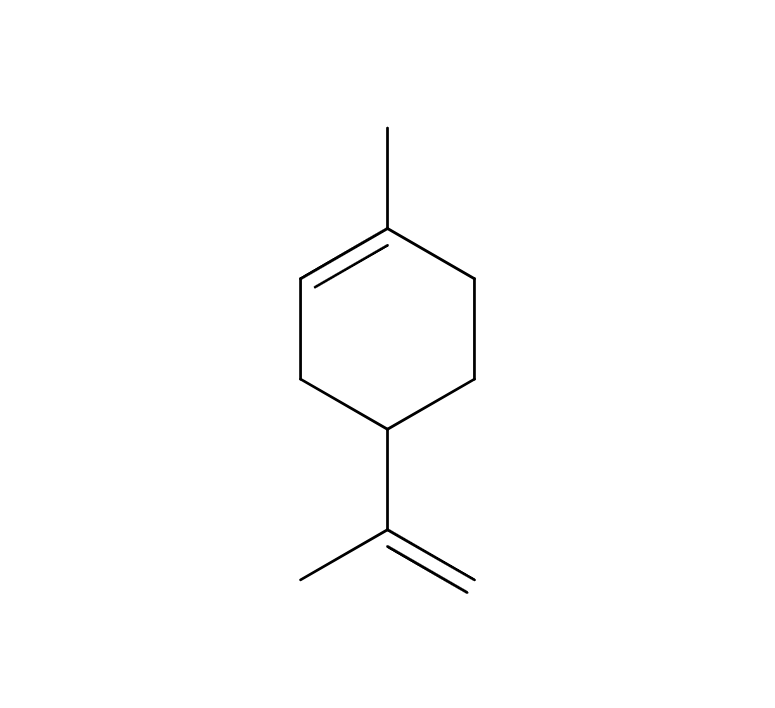
About 0.7% of Mandarin's essential oil is obtained by cold press from its peel, which is orange to slightly reddish in color.The yield is higher when grown in temperate regions with cooler temperatures. The main components include limonene, terpinene, and myrcene. The aroma is characterized by its depth, refreshment, and slight sweetness, with a subtle green undertone. It imparts a profound, clean, heartwarming, and gentle impression, occasionally with a slight hint of hardness. Fragrances can vary among manufacturers and batches, and some oils may appear slightly oily. Therefore, it's advisable to evaluate the fragrance before use. The scent can also differ depending the harvest time, whether the mandarins are red or green. Overall, it has a pleasant and familiar aroma that harmonizes well with many other essential oils. When blended with less favorable aromas or in situations where a blend doesn't harmonize well, Mandarin can contribute to creating a well-balanced aroma. The fragrance strength is weak, allowing for easy balancing by adding a little more to achieve the desired blend.