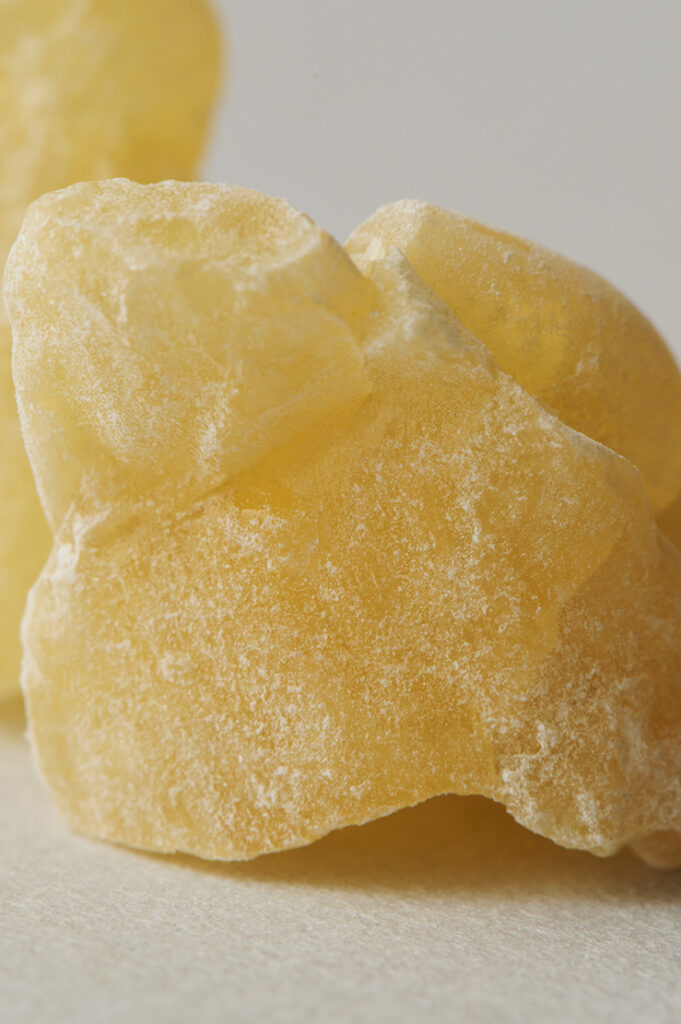
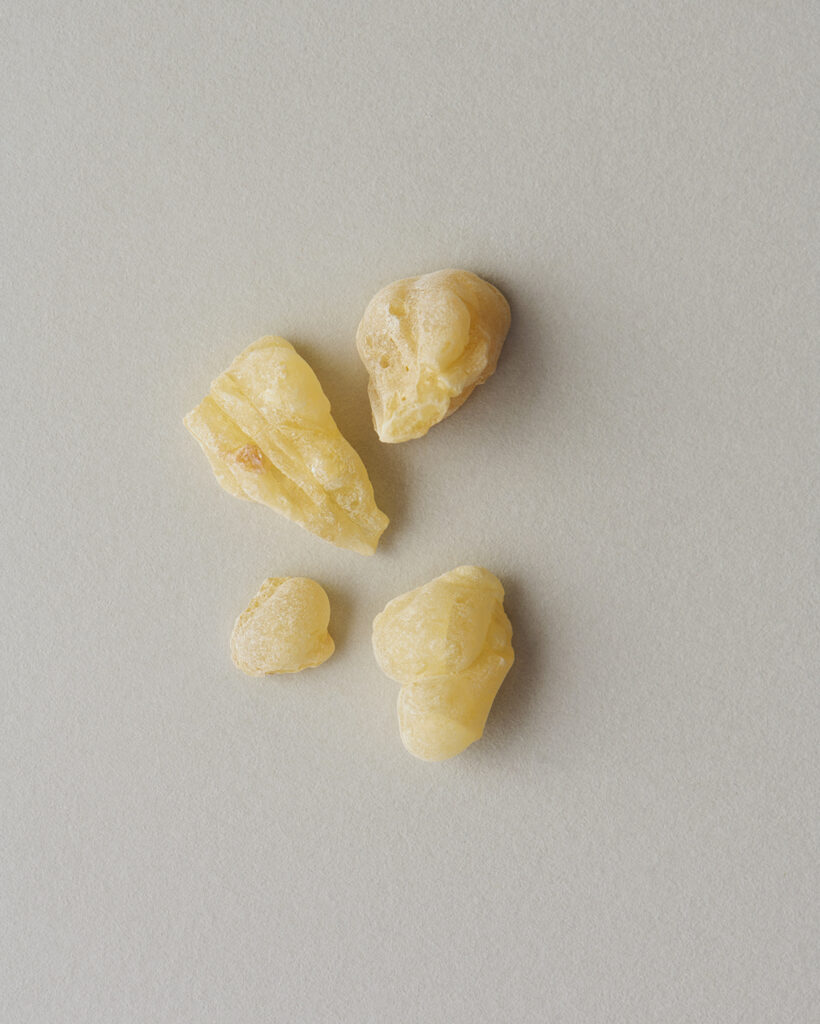
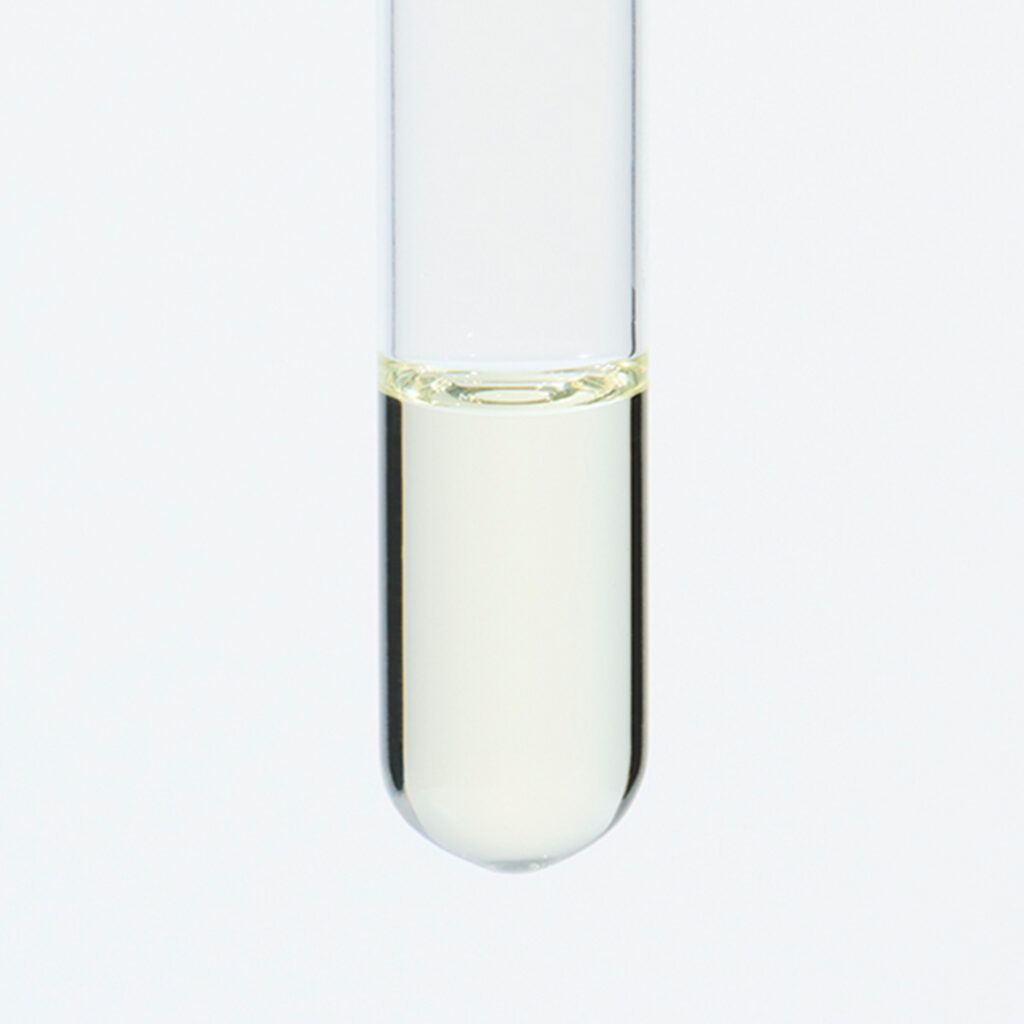
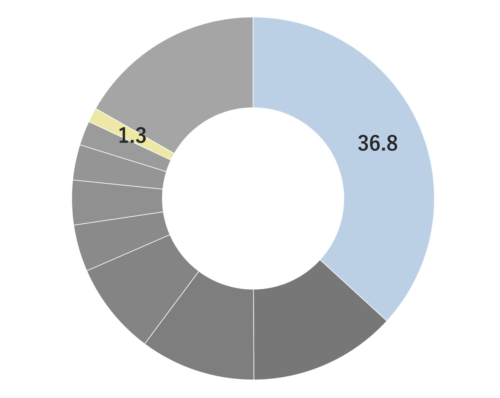
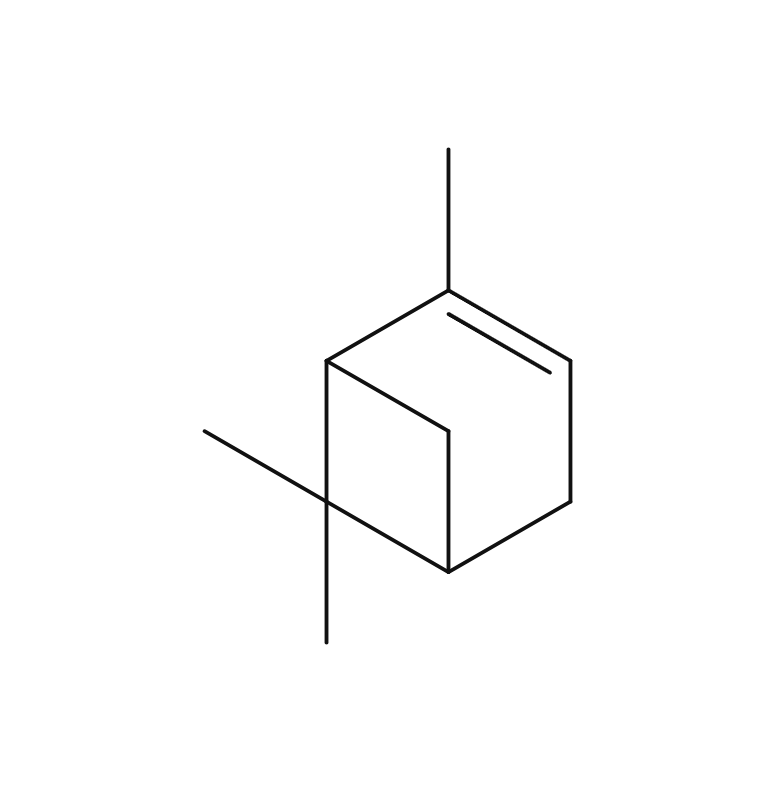
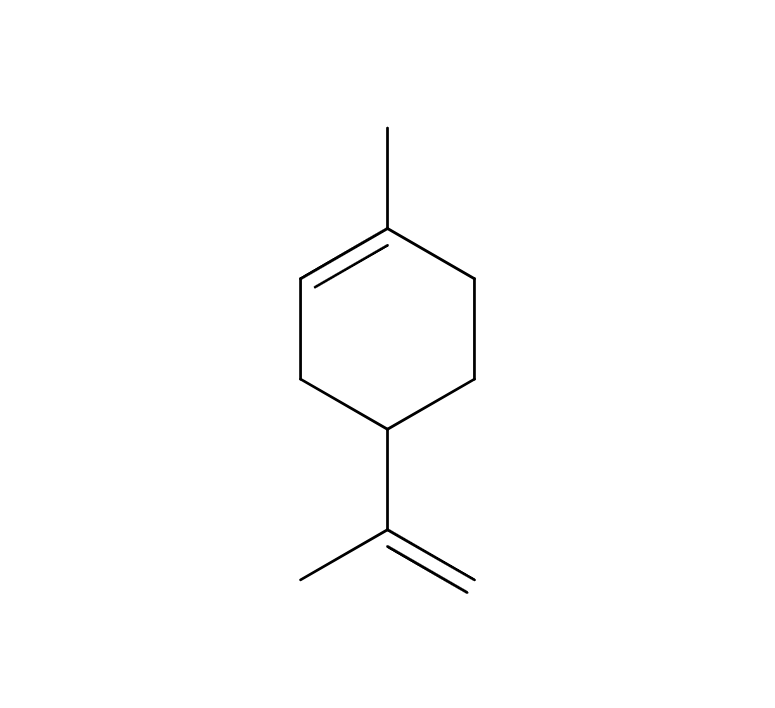
About 4-6% Frankincense essential oil is obtained by steam distillation from its dried resin, and has a pale yellow color. The main components are α-pinene, β-pinene, etc. which are often associated with the scents found in forest environments. Initially, the fragrance is fresh and reminiscent of a forest, but over time, it develops into a smoky, slightly sweet aroma with deep resinous notes reminicsent of pepper and citrus fruits. This fragrance is clear and pure, exuding a profound sense of divinity and tranquility. It blends harmoniously with a wide range of other essential oils, imparting a sophisticated character to the blend. It particularly complements deep and woody fragrances such as Petitgrain, Tea Tree, and Laurel. Additionally, it can be combined with citrus notes like Lemon and Grapefruit or invigorating scents like Eucalyptus for a clear and balanced aroma. Given its relatively mild scent, adding a bit more to the blend can help maintain a well-balanced scent.