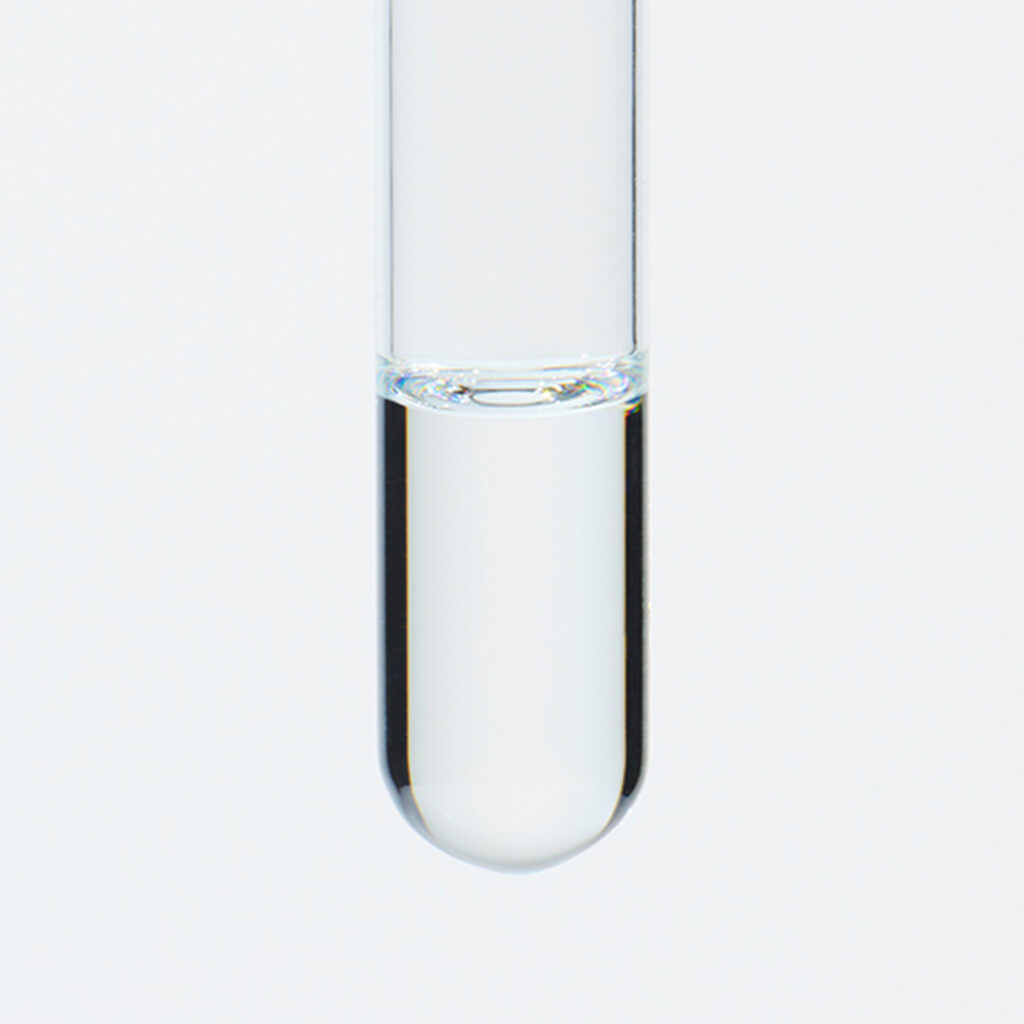
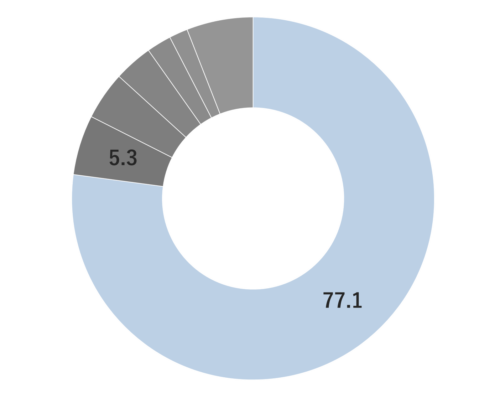
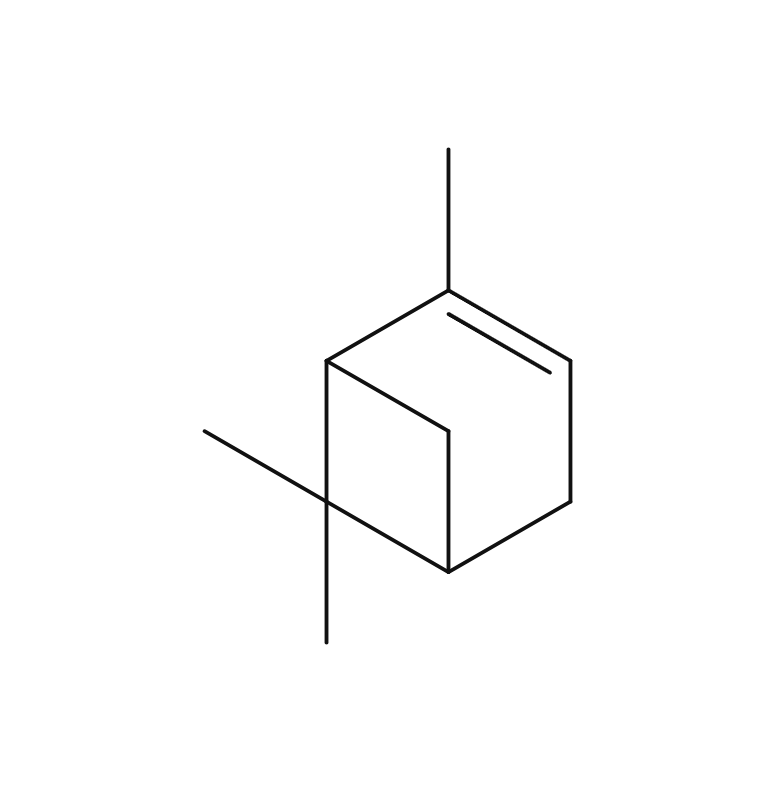
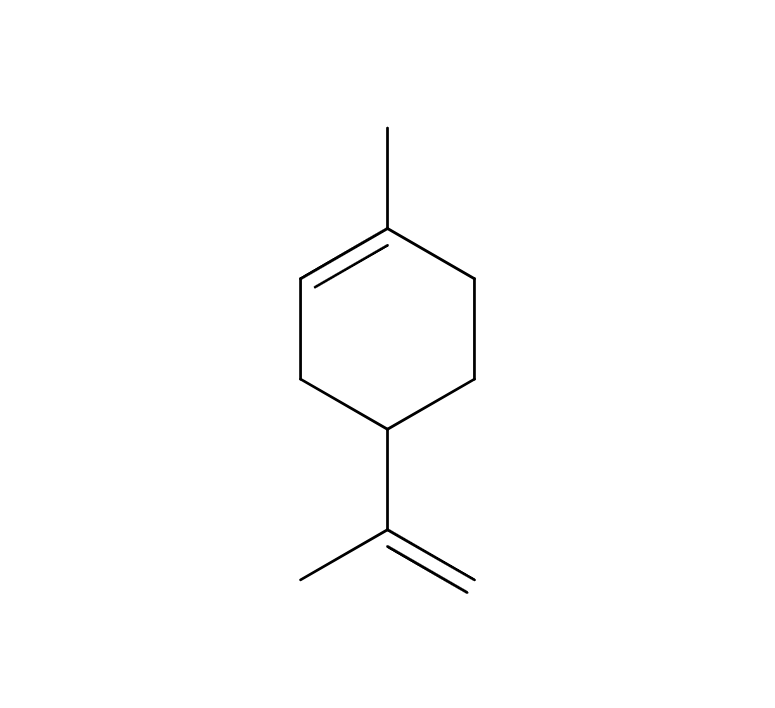
Approximately 2.5-6.0% of Fennel essential oil is obtained through steam distillation of its fruit, resulting in a clear to slightly yellowish color. The predominant component of this oil is anethole, which is known for its sweetness, being approximately 13 times sweeter than sugar. Trans-anethole, a constituent of the oil, is sometimes used as a food flavoring. Its aroma is reminiscent of anise, featuring a slightly intoxicating, penetrating, herbal sweetness and a cool, refreshing quality. It blends harmoniously with various essential oils, particularly citrus oils like Sweet Orange and Bergamot, as well as sweet-scented oils such as Sandalwood, Geranium, and Palmarosa.Due to its relatively strong fragrance, it is advisable to add it gradually when blending to achieve a balanced scent.