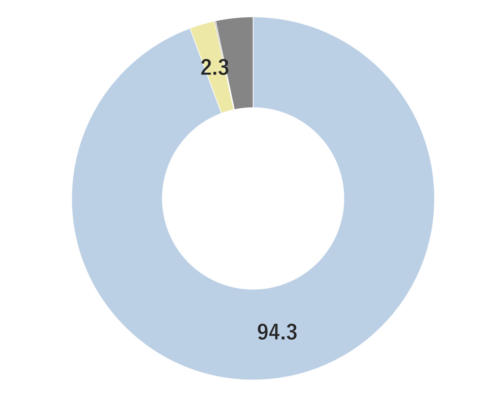
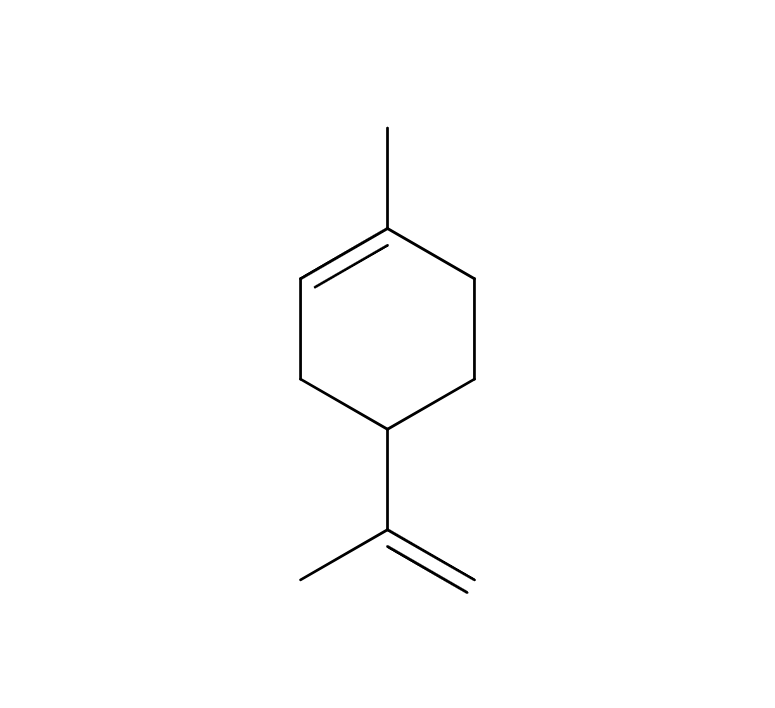
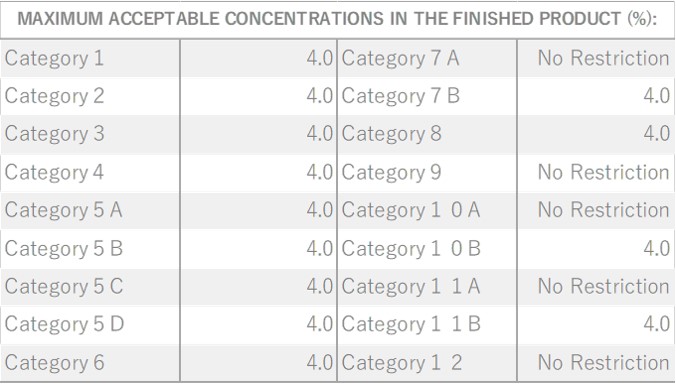
Grapefruit belongs to the Rutaceae family and grows up to 12 meters. Its leaves are dark green, oval, and arranged alternately, while the plant bears fragrant, cream-colored flowers. The fruit, after which it is named, grows in clusters similar to grapes. Grapefruits are typically yellow in color, combining sweetness and tartness with a slight bitterness. Varieties include white-fleshed, light red-fleshed, and red-fleshed, as well as nucleate and non-nucleate types. Among these, the colored non-nucleate variety is favored for fresh consumption, whereas the white-fleshed non-nucleate variety is preferred for processing.
Historically, Grapefruit cultivation is believed to have originated in the 18th century on the island of Barbados in the West Indies. The cultivation expanded to Florida in the United States around 1823, and commercial production thrived in Florida by 1930. In the United States, Grapefruit is a popular fruit and serves as the largest supplier of grapefruit oil.